The marketing mix (4Ps) considers the product, price, place and promotion (figure 1). The framework was developed by Jerome McCarthy in 1960 to formulate and implement marketing strategy.1 The framework was improved to consider customer service and service delivery by including people, process and physical evidence.2 An increased focus on relationships contributed to by the internet led to the addition of partnerships to the marketing mix. Partnerships allow organisations to work together to promote each other via a formal or informal agreement.3 The marketing mix has been suggested to not be customer centric and a customer focused framework (4Cs) was developed considering customer needs/wants (product), cost to customer (price), convenience (place) and communication (promotion).4
 Figure 1: Marketing mix (4Ps)1
Figure 1: Marketing mix (4Ps)1
The internet influences all facets of the marketing mix for products and services. The internet can be used for market research, to reach new customers and markets, alter business model, better serve customers and tailor offering, distribute products quicker and through new channels, engage with customers and communicate more effectively with partners like suppliers.5,6 This blog post will consider the implications of the internet on the marketing mix components product, price, place and promotion.
Product
Product considers the features of a product, service or brand and involves researching customer needs and using this information to modify existing products or develop new products to meet these needs.5,6 The core product is the essential benefit of product to meet customer needs whereas extended product includes additional benefits which may differentiate offering from competitors.3,5,6 A website can provide information on these features, collect information on customer preferences and allow feedback and product reviews.
The internet allows the core product to be changed into digital products or services. For example, iTunes and Spotify allow music downloads and streaming, Amazon sells electronic books which can be read using a Kindle (electronic reader), and newspapers provide online access to content (Figure 2 and 3). Previously, customers would buy physical music album compact disc and hard copy books and newspapers.
Figure 2: iTunes and Spotify logos2,3
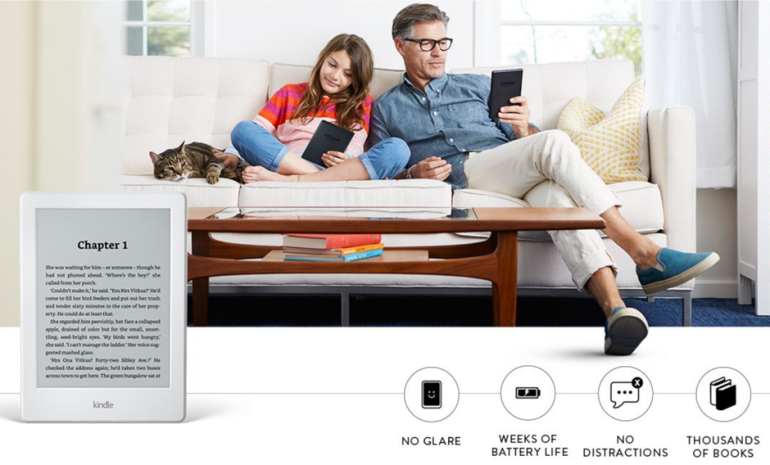 Figure 3: Amazon Kindle4
Figure 3: Amazon Kindle4
The internet allows businesses to offer unique value to customers. The internet allows mass customisation of products tailored for individual customers. Allowing businesses to sustain the resulting competitive advantage as initially it may be difficult to implement but differentiates offering from competitors.6 Apple allow customers to customise computers via website (figure 4). The internet allows businesses to use bundling to create value. Virgin Australia uses website to offer additional travel services like insurance, accommodation, car hire and loyalty points when customers purchase airfares online. This extends the core product of airfares (air transportation), utilises the benefits of bundling and provides customers convenience (figure 5).
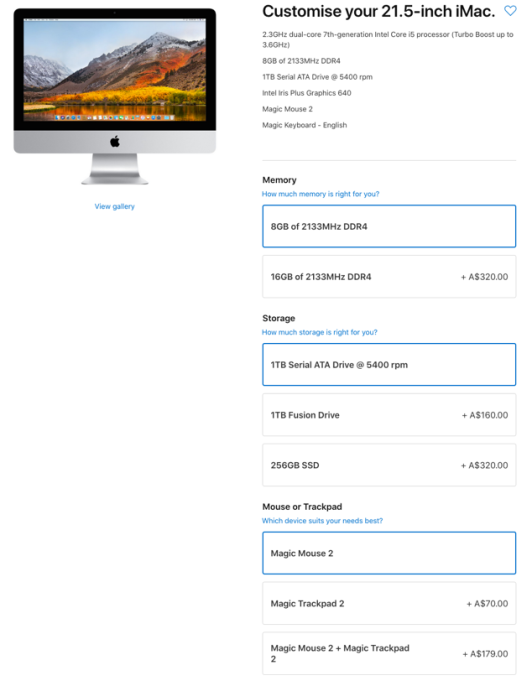
Figure 4: Customise Apple computer5
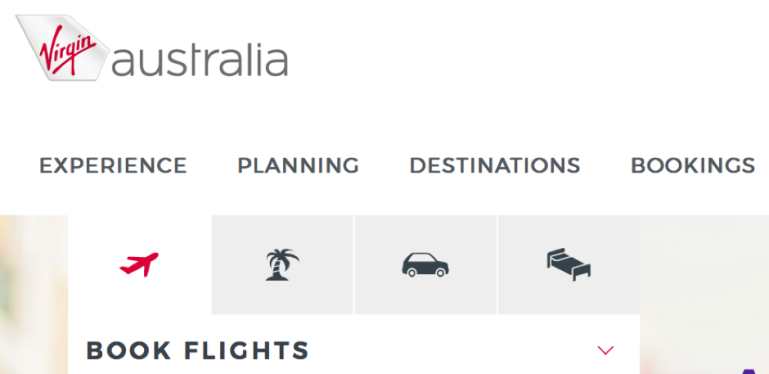
Figure 5: Virgin Australia booking options6
Price
Price considers the business pricing policy/ies, pricing model/s used and setting prices for products and services.3,5,6 The internet provides customers enhanced knowledge of pricing information leading to price transparency.3,5,6 This is assisted by price comparison websites. This increased knowledge may impact a business using differential pricing for different markets or customers as may be considered price discrimination.3
The internet reduces barriers to entry and allows businesses to access new markets increasing competition.6 The internet provides competitor information quicker and more transparently.5 Internet technologies can reduce operating and variable costs.5,6 These factors put pressure on businesses to lower prices leading to a focus on price rather than differentiation. Other factors which may impact price include product lifecycle (decreasing through cycle) and price sensitivity or elasticity of product.5,6
The internet allows auction and dynamic pricing strategies to be applied easier. Internet technology allows auction sites like eBay extend the end time if a bidder places a bid near finish allowing others time to respond (figure 6).3 Dynamic pricing allows prices to be changed in real time depending on demand or market forces and is commonly used by ticketing, grocery and accommodation businesses. Online businesses may use penetration pricing to develop market share and acquire customers but may need to be sustained to retain them. They may use premium pricing to portray a higher quality product. Due to increased competition online competition-based pricing may be used on popular products and target-profit (breakeven) pricing for less popular products.3 The internet allows other pricing strategies like shipping fees, bundling and discounts for digital product/service versions.3,5,6
 Figure 6: eBay logo7
Figure 6: eBay logo7
Place
Place considers the distribution of product to customers. The internet removes geographical barriers providing customers with more options and businesses with more competitors. Key distribution benefits of the internet are speed, flexibility and convenience.5,6 The internet allows electronic transactions to be tracked by customers and improves the supply chain with better efficiency and inventory control. Websites may be positioned towards buyers, sellers or be neutral.3 A website can be localised to a specific region taking into account cultural factors and/or different product needs.3
The internet allows businesses to sell direct to customers by removing intermediaries (disintermediation) like distributors, wholesalers or retailers. For example, Dell sells computers direct to customers (figure 7). However, businesses should consider if the expertise, market knowledge and customer service provided by intermediaries will be difficult to replicate and if any conflicts may arise due to existing agreements/partnerships.7
Figure 7: Dell computer8
Another option involves the creation of new intermediaries. Examples include the use of affiliates to direct customers to an electronic commerce site or customers using a comparison website to assist purchase decision or facilitate purchase. These intermediaries receive a commission from each successful transaction they facilitated.7 Businesses can use intermediaries to reach more customers. Wotif is an example of an intermediary that allows customers to purchase accommodation, flights and hire cars (figure 8). The value and competitive advantage provided by intermediaries should be considered.7
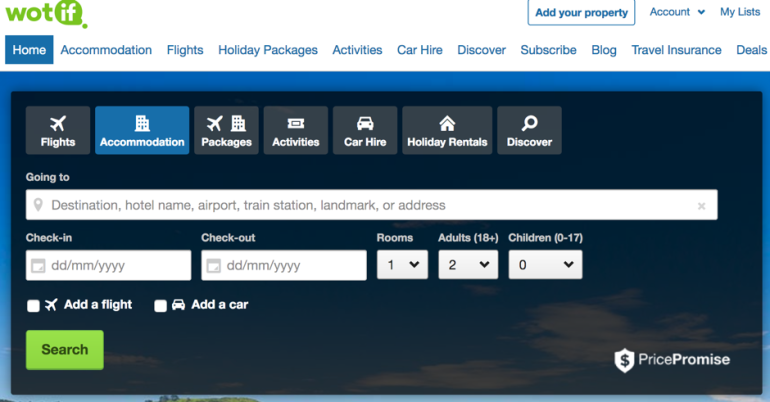 Figure 8: Wotif homepage9
Figure 8: Wotif homepage9
The internet allows businesses to operate as a virtual organisation without defined boundaries and may form strategic alliances/partnerships with other organisations to outsource certain activities.3,8 For example, the internet allows businesses to partner with Google to use AdWords or affiliates to generate traffic to website or secure payment system to facilitate electronic transactions.
Promotion
Promotion utilises marketing communications to advise customers about organisation and develop brand/product awareness. The internet influences how customers and businesses communicate, the channels this occurs and allows two-way communication. The internet can influence different parts of the buying process by generating awareness, providing product information, lead generation, assist purchase decision, facilitating purchase and feedback. The internet allows promotional activities to be targeted and personalised.
The internet can influence how promotion tools are used (figure 9). Advertising may involve website display ads or pay per click search advertising like AdWords. Personal selling through website chat bots and affiliate marketing. Sales promotion through online incentives, discounts and loyalty programs. Online public relations through electronic newsletters, blogs, social media and editorial content. Direct marketing through opt in email messages like newsletters and can be personally tailored. These tools can be used to attract and retain customers.
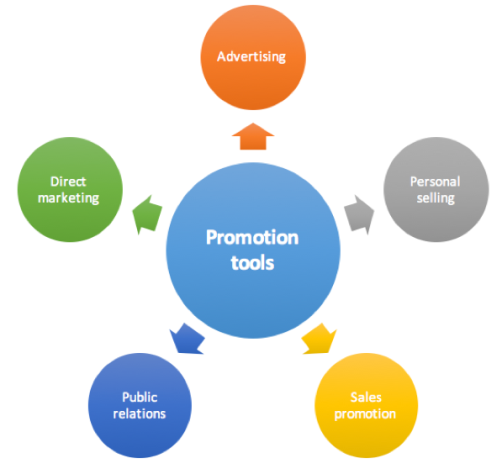
Figure 9: Promotion tools10
Print media and television may be used to complement online promotion or direct customers to website. Multiple electronic platforms may be used for promotion such as website and social media. Consequently, is it important to integrate promotions in online and offline environments to leverage the benefits each provide into a multi-channel strategy.
What are your thoughts on the impact of the internet on the marketing mix?
References
- McCarthy J. Basic marketing: a managerial approach. Homewood: RD Irwin; 1960.
- Booms B, Bitner M. Marketing strategies and organisation structures for service firms. In: Donnelly J, George W, editors. Marketing of services. New York: American Marketing Association; 1981.
- Chaffey D, Ellis-Chadwick F. Digital marketing: strategy, implementation and practice. Harlow: Pearson; 2016.
- Lautenborn R. New marketing litany: 4Ps passes; C-words take over. Advertising Age. 1990;10:26.
- Nezamabad MN. The impact and benefits of internet on marketing mix. Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences. 2011;5(9):1784-89.
- Porter ME. Strategy and the internet. Harvard Business Review. 2001;Mar:63-78.
- Gay R, Charlesworth A, Esen R. Online marketing: a customer-led approach. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 2007.
- Kraut R, Steinfield C, Chan A, Butler B, Hoag A. Coordination and virtualisation: the role of electronic networks and personal relationships. Organization Science. 1999;10(6):722-44.
Images
- Brennan Q. Marketing mix [image]. Queanbeyan: Quinton Brennan; 2018
- Apple. iTunes [Internet]. Sydney: Apple; 2018 [cited 2018 Sep 13]. Available from: https://www.apple.com/au/itunes/
- Spotify. Spotify Website [Internet]. Stockholm: Spotify AB; 2018 [cited 2018 Sep 13]. Available from: https://www.spotify.com/au/
- Amazon. A book lover’s best friend [photograph on the Internet]. Seattle: Amazon; 2018 [cited 2018 Sep 13]. Available from: https://www.amazon.com/gp/product/B00ZV9PXP2/?ie=UTF8&ref_=topnav_storetab_kstore
- Apple. Customise your 21.5-inch iMac [Internet]. Sydney: Apple; 2018 [cited 2018 Sep 13]. Available from: https://www.apple.com/au/shop/buy-mac/imac/21.5-inch-2.3ghz-1tb
- Virgin Australia. Virgin Australia Website [Internet]. Bowen Hills: Virgin Australia; 2018 [cited 2018 Sep 13]. Available from: https://www.virginaustralia.com/au/en/
- eBay. eBay Website [Internet]. [place unknown]: eBay; 2018 [cited 2018 Sep 13]. Available from: https://www.ebay.com.au/
- Dell Australia. Dell Website [Internet]. Frenchs Forest: Dell Australia; 2018 [cited 2018 Sep 13]. Available from: https://www.dell.com/en-au#
- Wotif. Wotif Website [Internet]. [place unkown]: Wotif; 2018 [cited 2018 Sep 13]. Available from: https://www.wotif.com/
- Brennan Q. Promotion tools [image]. Queanbeyan: Quinton Brennan; 2018






Hi Quinton,nice work!
If you have time, can visit my site.
https://phoebeinternetmatketing.wordpress.com
Thank you!
LikeLiked by 2 people
Thanks
LikeLike
Nice read. Thanks for sharing this
LikeLiked by 2 people
Thanks
LikeLike
nice work
LikeLiked by 2 people
Thanks
LikeLike
I like your analysis structure.
LikeLiked by 2 people
Thanks
LikeLike
I like your example.
LikeLiked by 2 people
Thanks
LikeLike
good work
LikeLiked by 2 people
Thanks
LikeLike
Well presented, thanks
LikeLiked by 2 people
Thanks
LikeLike
Well done.
LikeLiked by 2 people
Thanks
LikeLike
Well done
LikeLiked by 2 people
Thanks
LikeLike
You have used the proper way to describe the internet impact the marketing mix, thanks
LikeLike
Nice post. Value drives Growth, and Value is determined by Need. Fill the Need, you create Value, which then builds Growth. And that’s a good thing! 🙂 Kind Regards, Steve
LikeLike